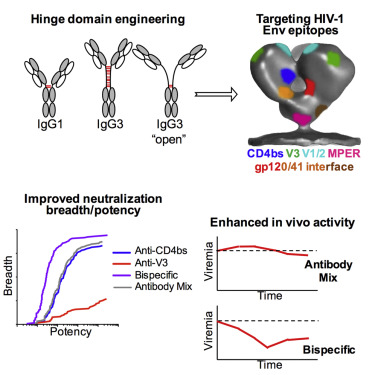
強化された幅と能力をもつ二重特異性抗HIV-1抗体
HIV-1エンベロープ糖タンパク質(Env)に対する広域中和抗体(bNAb)は、HIV-1の動物モデルとヒトのウイルス血症を抑える。
ウイルスのエスケープ変異体を出現させることなく強い活性を得るためには、ウイルス適合に必須な異なるエピトープをターゲットとするために、異なるbNAbを同時投与する必要がある。
ここでは、強力な活性をもった二重特異性の抗Env中和抗体(biNAb)の開発について報告する。
BiNAbの相乗的な活性は、設計されたIgG3のヒンジドメインを組み合わせることによって、IgG1-Fcの機能特性を保持しながらEnv三量体にヘテロ二価結合するために必要な、Fabドメインの柔軟性を増加することで獲得された。
修飾していないbiNAbと比較すると、ヒンジドメインの変異体は十分に改良された中和活性を発揮しており、インビトロでの相乗的な中和能や、生体内での治療活性の強化をHIV-1を感染させたヒト化マウスで示した。
これらの発見は、中和の幅と能力が強化されたbiNAbを生み出す革新的な戦略を示唆するものであり、HIV-1感染をコントロールするための理想的な候補分子を意味している。
Bispecific Anti-HIV-1 Antibodies with Enhanced Breadth and Potency
Broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) against the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein (Env) suppress viremia in animal models of HIV-1 and humans. To achieve potent activity without the emergence of viral escape mutants, co-administration of different bNAbs is necessary to target distinct epitopes essential for viral fitness. Here, we report the development of bispecific anti-Env neutralizing antibodies (biNAbs) with potent activity. Synergistic activity of biNAbs was achieved by combining an engineered hinge domain of IgG3 to increase Fab domain flexibility necessary for hetero-bivalent binding to the Env trimer while retaining the functional properties of the IgG1-Fc. Compared to unmodified biNAbs, hinge domain variants exhibited substantially improved neutralization activity, with particular combinations showing evidence of synergistic neutralization potency in vitro and enhanced in vivo therapeutic activity in HIV-1-infected humanized mice. These findings suggest innovative strategies for generating biNAbs with enhanced neutralization breadth and potency, representing ideal candidate molecules for the control of HIV-1 infection.
-Volume 165, Issue 7, p1609–1620, 16 June 2016 Cell